Ça peut aussi vous intéresser
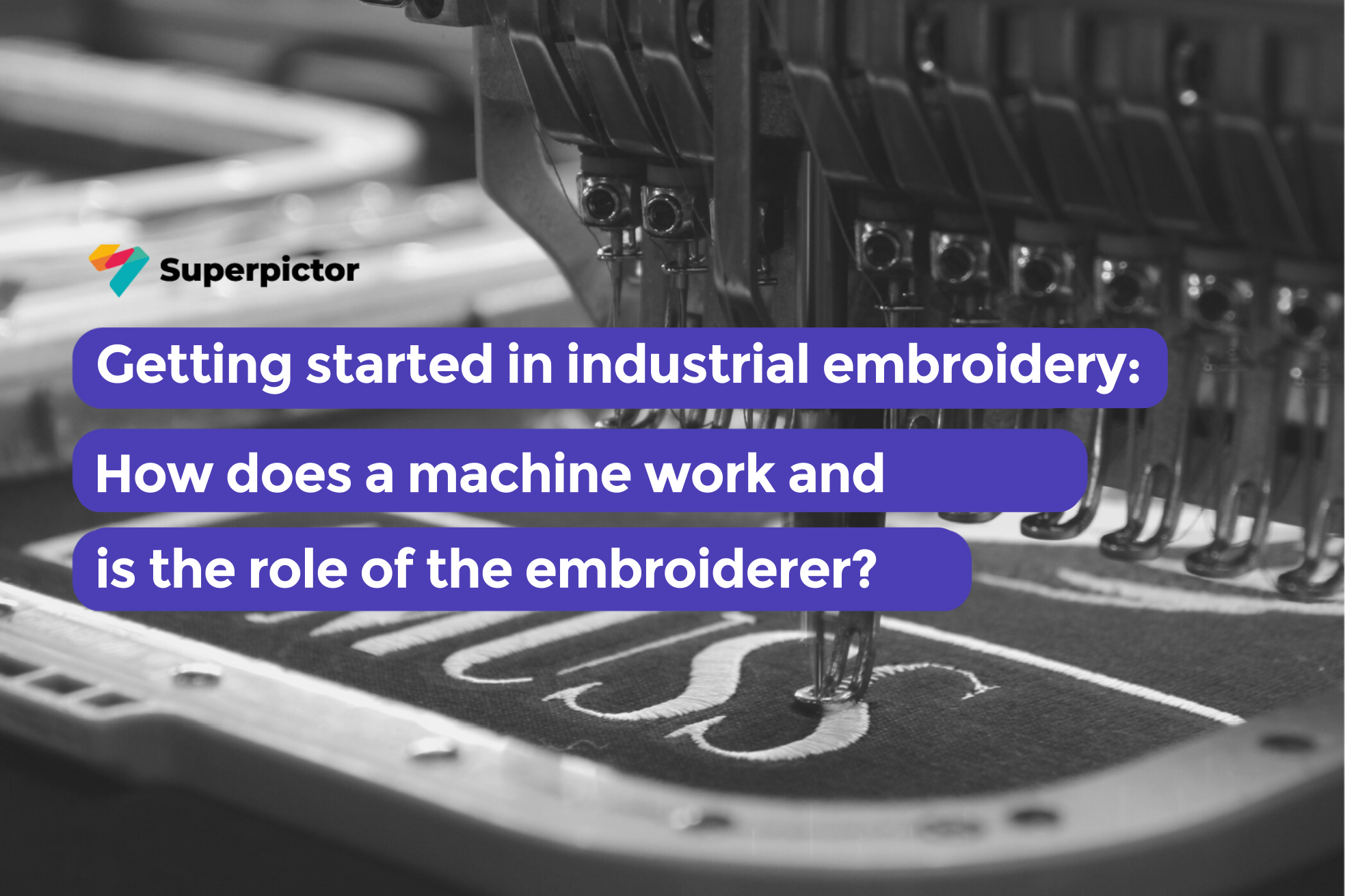
Getting started in industrial embroidery: how does a machine work and what is the rôle of the embroiderer?
28 avril 2023Embroidery is the art of creating decorative patterns with threads using a needle on fabric or other materials. It can be done by hand or with the help of an embroidery machine.
Producing large quantities of embroidered pieces requires industrial embroidery machines, which typically have between 1 and 12 embroidery heads.
To do so, the operator(s) must be trained on the entire machine park, follow manufacturing procedures, and have acquired professional know-how.
But how does an embroidery machine actually work, and what is the role of the embroiderer in production? These are two questions that arise when starting embroidery and making it a professional activity.
How does an industrial embroidery machine work?
Whether an embroidery machine has 1 or 12 heads, it always works the same way: the thread always follows the same path from the spool to the needle to stitch the material.

Embroidery thread path
- Each thread line, coming from the coil, passes through a tube to reach the first tensioning block: this is what will adjust the thread tension according to the embroidery support or the specific thread.
- After passing through the first tensioning block, it goes through a rotating sensor that will check if the thread is unwinding continuously. If the sensor blocks, it means that there is no more thread or that the thread has broken.
- After passing through the sensor, the thread will go through a second tensioning block with a spring that will give some slack to the thread.
- The thread then passes through the arm and a thread clip to ensure that it does not move and remains in place.

Embroidery thread path
5. The thread ends its path through the needle and the presser foot before going to stitch the fabric. The needle must be sharp enough to properly pierce the fabric. The presser foot will press down on the fabric so that at the moment the thread pierces the fabric, it is held securely in place.

Needles and presser feet of a Barudan embroidery machine.
6. Finally, there is the non-visible part of the embroidery machine: the essential bobbin. It is thanks to this part that the embroidery is sturdy, as it will create the knot between the upper thread from the spool and the inner thread, the bobbin thread. This is the thread that can be seen on the back of the embroidery. Without it, the embroidery would not hold up over time!

Bobbins of a 6-head Barudan embroidery machine.
What is the role of an embroiderer in a machine park?
Industrializing embroidery could lead to the belief that the embroiderer is not very useful behind their machine. Think again! The embroiderer is very important and without them, production could not run.
A professional embroiderer regularly performs the following tasks:
1. Receive and verify the customer's file: production sheet, proof and technical sheets.
See also: Configure a product and generate a proof with Superpictor.
2. Receive and verify the items to be embroidered: conformity of references, colors, and sizes.
3. Hoop the products or prepare the embroidery flat.
4. Program the different technical information of the designs on the machine: sequences and threads.
See also: Order an embroidery program with Superpictor.
5. Embroider while monitoring the technical and aesthetic qualities of the embroidery.
6. Check the proper operation of the machine, change bobbins and check thread availability, and reposition the thread breaks.
7. Finish the embroidery: paper and threads.
8. Sort the embroidered clothes by size for shipment.
9. Maintain the machines and clean the work area.

Embroidery is a profession that is learned on the job: experience is paramount! This experience allows one to step back and solve the various problems that can be encountered on a machine.
See also: The 6 most common mistakes when starting embroidery.
A question?
Ask for advice from one of our experts.
👉 Get in touch with a Superpictor advisor.
Did you like this article?
Don't miss the next ones by receiving them directly in your inbox.